The five key principles for soil health
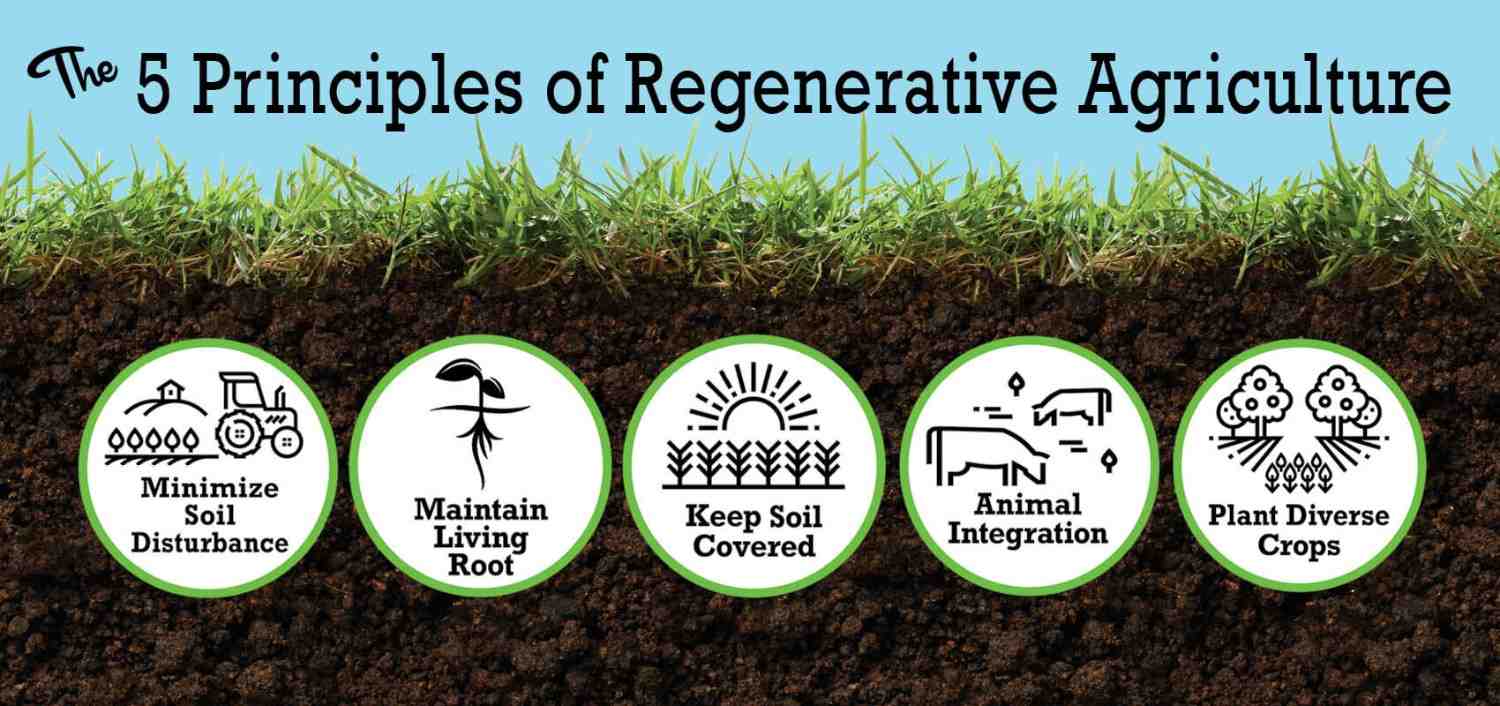
I’ve explained that regenerative agriculture involves farming principles and practices that enrich soils, boost biodiversity, improve watersheds, and enhance ecosystem services. To protect soil according to regenerative agriculture’s objectives, focus on the five key principles for soil health activities:
Minimize soil disturbance
Soil contains a complex network of worm holes, fungal hyphae, and a labyrinth of microscopic air pockets surrounded by soil particle aggregates. Once you establish a bed, you leave its surfaces undisturbed. Over time, watering and soil organisms’ activity transform the top layer into subsoil.
Enhancing Soil Health through Regenerative Agriculture Techniques
However, ploughing or applying heavy doses of fertilizer disrupts this natural process and increases the risk of soil erosion. Additionally, storing or throwing plastic materials under the soil, based on the myth that they will decompose, worsens the problem. To counter these issues and enhance soil health, regenerative agriculture employs several key techniques. These include no tillage, cover crops, rotational cropping, reduced use of chemical inputs, and the integration of plants and animals. Furthermore, these practices work synergistically to restore and maintain the natural balance of the soil ecosystem.
Minimize the use of chemical inputs:
Chemicals damage soil organic matter and fertility, reduce biodiversity, and increase CO2 emissions. In contrast, regenerative agriculture employs a whole ecosystem approach, working with nature rather than against it. Consequently, farmers consider the entire farming ecosystem when making management decisions.

Keep living roots in the soil:
Keeping live roots in the soil is essential for high-functioning soil. Plant roots nourish soil microbes, which then support the roots. Plants invest significant energy into cultivating and feeding beneficial soil microbes through their root exudates. In return, these symbiotic microbes nourish and protect the plants. Consequently, roots play a crucial role in crop growth by absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. Its important elements under the five key principles for soil health.
Keep the soil surface covered:
Covering the soil surface plays a crucial role in regenerative agriculture. In conservation agriculture, maintaining a permanent soil cover is essential. This practice not only protects the topsoil from erosion caused by wind and water but also prevents the loss of valuable organic matter. Furthermore, it helps maintain soil moisture, suppresses weed growth, and contributes to nutrient cycling. In addition, it enhances soil structure and supports biodiversity, ultimately leading to healthier and more resilient agricultural systems.
The more common regenerative farming methods include:
No-till systems
which heavily reduce the digging and ploughing that can lead to loosened topsoil being blown away by wind or carried away by water.
Cover crops
which are grown after the main commercial crop has been harvested, and can be grazed by livestock or harvested themselves.
Increasing biodiversity
which increases the variety of nutrients going into the soil through roots and natural decomposition and, if well-managed, attracts insects that are natural predators of pests.
Rotating crops
so that what is being taken out and put into the soil naturally by plants is balanced.
Integrating livestock
to combine animals and plants in a single ecosystem.
Minimizing chemical inputs
to minimize negative impacts on biodiversity and pollution of waterways due to runoff.
Animal integration:
About 60 percent of the world’s agricultural land is grazing land, supporting approximately 360 million cattle and over 600 million sheep and goats. Significantly, animal grazing contributes to soil health by controlling the growth of dominant plant species. Consequently, this process allows less competitive species to establish themselves. Furthermore, animal droppings enrich the soil with nutrients, which, in turn, promotes plant growth.
5. Plant diverse crops:
A diverse range of crops improves soil quality by replenishing nutrients. For example, crop plants deplete the soil’s nitrogen. To restore this nitrogen, farmers plant leguminous plants. These plants host bacteria that convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds, which crop plants then utilize. Furthermore, the following steps further enhance soil health:
Enhancing soil health
- To maintain soil fertility, rotate crops regularly.
- Additionally, plant grassland strips within and along fields to protect soil and reduce erosion.
- Furthermore, establish wildlife habitats near fields to promote biodiversity.
- Moreover, reduce tillage to preserve soil structure.
- Enrich soils with organic matter to boost nutrient levels as well.
- Additionally, use multiple cropping or intercropping to diversify plant inputs.
- Finally, implement agroforestry practices to integrate trees and shrubs.


Pingback: The Passionate on Regenerative Farming - Carbon Revolve
Pingback: How to Make Sustainable Rooftop Gardening? - Carbon Revolve
Pingback: Key Practices on Regenerative Agriculture - Carbon Revolve