Be a Small Farm Consultant
Biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem stability, resilience, and providing resources essential for human survival and well-being.
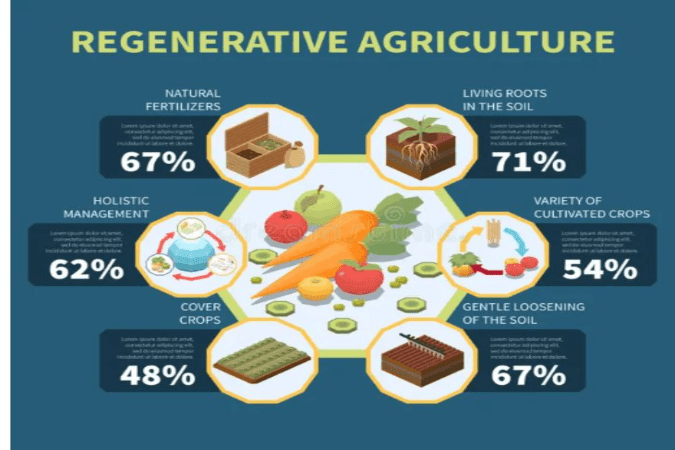
Regenerative Agriculture Definition
Plants capture atmospheric carbon to build organic biomass. Soil organisms release CO2 back into the atmosphere by breaking down the biomass. The soil sequesters only 2-4% of carbon from the organic biomass as humus and glomalins. Green plants create a barrier between air and soil, reducing carbon emissions by microbes. Organic matter (humus), clay, and biochar carry a negative charge. Regenerative agriculture have high cation exchange capacity, holding cations like Ca++, Mg++, K+, and providing them to roots in exchange for NH4+, Al+++, and H+.




What Is Soil Level
Why Do Plants Release Sugars Into The Soil?
Millions of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and nematodes, eagerly await liquid carbon food. They rush to the root zone, known as the rhizosphere, colonize it, and feed on carbon exudates. Soil organisms extract nutrients from soil minerals and supply plants with nutrients and hormones to keep them healthy and encourage continued liquid carbon release. Saprophytes feed on dead organisms. Microbe-rich organic soils help humanity by degrading plant and animal biomass, fixing carbon as humus and glomalin, which remain stable for centuries. Healthier plants release more liquid carbon, leading to increased glomalin, humus, and suberin.
Regenerative Farming Practices
Soil Enrichment

Soil quality can be improved by using crop residues after harvest, plowing in cover crops, or adding compost. Plants depend on soil microorganisms for growth, which chemical fertilizers and pesticides destroy. Instead of using many pesticides, it is also possible to use pest killers from birds, spiders, and insects.
Permaculture

Permaculture is based on creating permanent agricultural systems through a combination of agroforestry, grasslands, vermicomposting, rainwater harvesting, sheet mulching with biological matter, and creating structures that build soil fertility.
Biodegradable

Biodegradable waste is decomposed by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and other organisms and materials derived from living organisms, including plants, food scraps, yard waste, and paper. The function of ecosystems and the natural cycling of nutrients are significantly impacted.
Biomimicry

Observing, sketching, and exploring living systems in the classroom can help you learn how they interact and thrive. Taking your students on a walk around your school or in a nearby park can also help them see their surroundings differently.
Cover Crop

The purpose of a cover crop is to prevent weeds from invading the soil and to prevent soil erosion caused by weeds. Green manure crops can be used as fertilizer, chopped down, plowed in, used as mulch, grazed as additional forage, or harvested for other uses.
Soil Service

Ecosystem services are a useful way for ecosystems to contribute to human well-being. Different types of organisms create diversity. How ecosystem services and biodiversity interact can quickly become uncertain. Come down the rabbit hole with me to see how biodiversity and ecosystem services go hand in hand.
Some Cover Crops Crossword Clue
Benefits of Cover Crops
Maintenance of soil fertility: After a cover cycle, cover crops act as manure and retain nutrients to prevent erosion, while legumes add nitrate directly to the soil.
Water regime management: Crop rotation with cover crops improves soil moisture management throughout the year.
Economic Impact of Sustainable Agriculture
3. Agroecological practices help maintain ecosystem services and protect predators.
4. Resilience to climate change: Sustainable agriculture reduces erosion and increases drought.
5. Greater opportunities and benefits to smallholder farmers through sustainable practices.
7. Nutrient-dense foods: Nutrient-dense crops are key to sustainable agriculture.
8. Transform sustainable agriculture into an efficient way to reduce industrial agriculture's transportation and food production needs.
9. Strengthening the local economy by increasing farmers' income: Sustainable agriculture can strengthen the local economy.
Comparative on Microbes Than Global People
The microbial of soil community is more than 90% bacteria and fungi by mass. Undisturbed soils like grasslands and forests benefit fungi whose thread-like hyphae remain undisturbed. Cultivation or the use of synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, however, reduces the fungal population.
The Soil Kingdom
The soil is a living kingdom that includes fungi, algae, bacteria, earthworms, termites, ants, nematodes, dung beetles, etc. About 90% of these are bacteria and fungi. All of them need carbon as a source of energy to feed, grow, and build their bodies. Most of that carbon comes from plants.
Healthy Soils
Absorb CO2 by plants, using sunlight and water to make sugars. What you may not know is that 20 to 40% of these sugars, amino acids, and carboxylic acids are released into the soil as liquid carbon. It is like the tax we pay to governments.
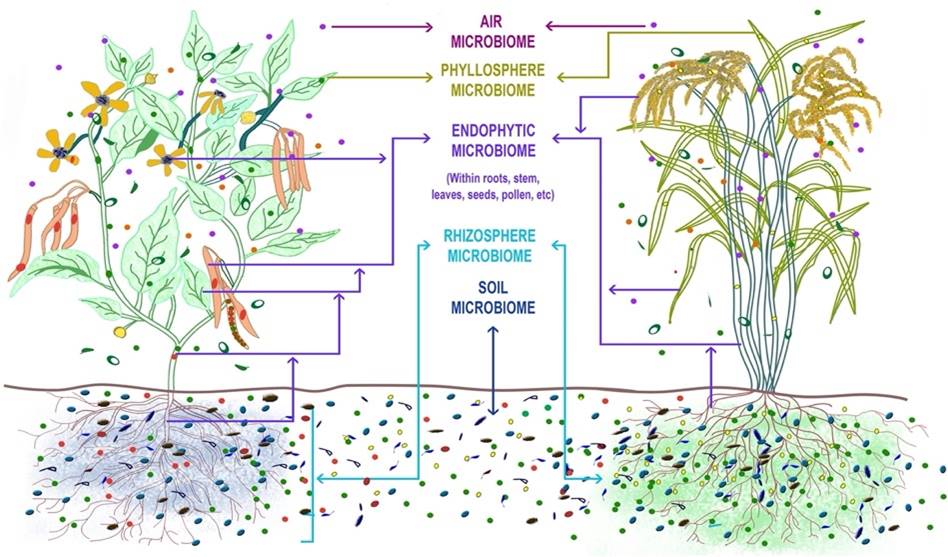
Plant Microbiome
Microbes are present everywhere. They are present in the air as the air microbiome, on the leaves as the phyllosphere microbiome, inside leaves as the endophyte microbiome, near the roots as the rhizosphere microbiome, and in the soil as the soil microbiome.
Carbon Dioxide Detector
Carbon Dioxide vs Carbon Monoxide
Oxygen travels between red blood cells primarily through iron (ferrous) molecules in the blood. Hemoglobin also carries CO2, but CO2 dissolves in blood plasma. The body exchanges oxygen for carbon dioxide through different processes. When a person inhales CO, hemoglobin accepts its CO molecule and becomes carboxyhemoglobin. Carbon monoxide forms a stable complex with hemoglobin (Hb) in red blood cells. This destroys the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity, leading to suffocation. In severe cases, complete blood transfusions can prevent death, but normal circulation must be restored after blood cells die. Oxygen gas can treat mild cases of CO poisoning, but it is ineffective for severe cases.


How does a composting toilet work
As a ship’s cook, I worked on boats with vacuum toilets that drained sewage into treatment systems: enzymes and air break down the coliform content in the treatment system. After treatment, it is pumped into the ocean as pure water, hopefully because pollution carries a large penalty. There are several types of composting toilets, and which one is best for your situation depends on the type. It’s a bucket toilet in a box with a nice toilet seat. Using this is super easy, super cheap, and super quiet. One can be made for under $20. Separation and everything else can complicate things.
Sustainable Farming Practices



What Is No Till Farming
Although often used interchangeably, no and no cultivation have different meanings. In a no-till field, the soil does not disturb the machine, but in a no-till field, there is little. In both methods, herbaceous plants control weeds, but no-tall is popular because it does not disturb the soil surface. The benefits of no-till include maintaining soil health and reducing erosion.
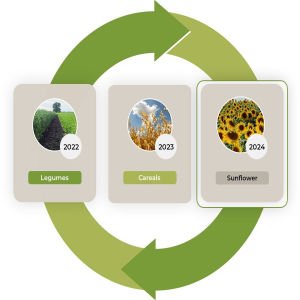
What Is Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is rotating crops within the same field to maintain soil fertility. The soil will likely become deficient in one particular nutrient if only one type of nutrient extraction habit is practiced. Saves soil by ensuring its conservation. We are reducing reliance on synthetic chemicals, Reducing pest build-up, Preventing diseases, and Controlling weeds.
What Is Biochar
Inoculating biochar involves soaking it in compost or worm tea and making charcoal from hardwood. After a few days, biochar forms and lasts hundreds of years in the soil. Farming with biochar offers immediate benefits. If not properly inoculated, it can temporarily worsen the soil, but it eventually balances out and begins delivering benefits.
What Is Agroecology
The branch in which it operates is agriculture. Culturing trees or shrubs around or among crops or pastures is known as agroforestry or agro-sylviculture. Planting shrubs and trees together for agricultural and forestry purposes. The result is an increase in tree cover.
- Farmer’s yield can be increased
- Reduce the chances of total los.
- To reduce soil erosion.
- The environment needs to be improved.
- It will help minimize the effects of climate change.
- Biodiversity improvement
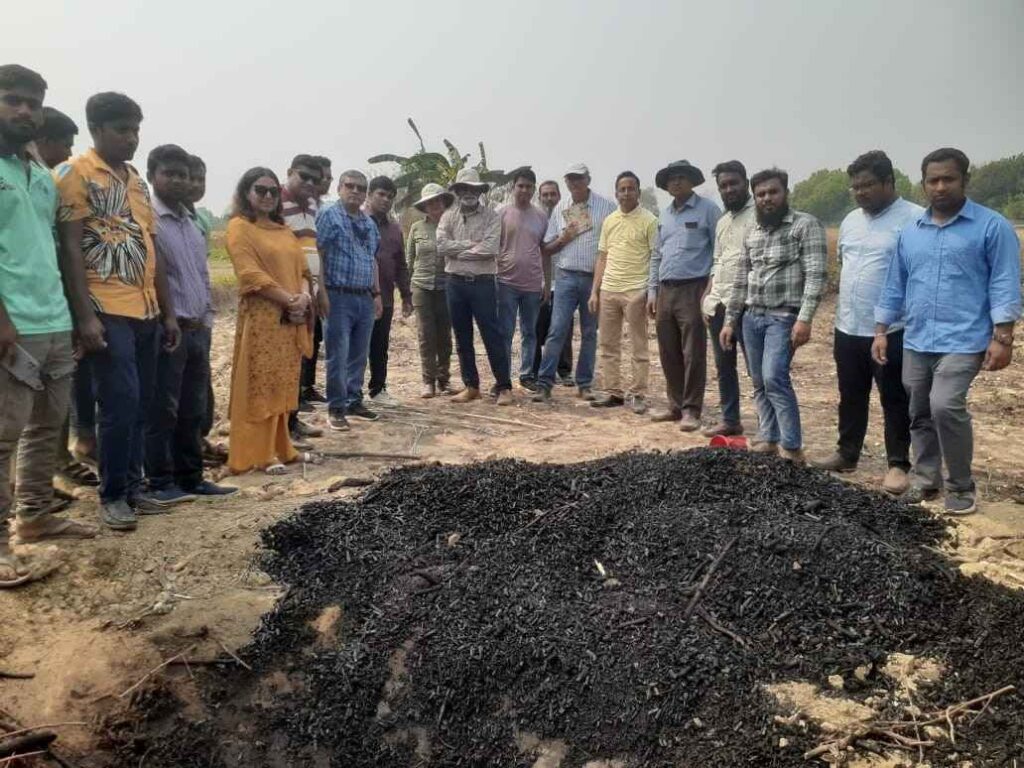
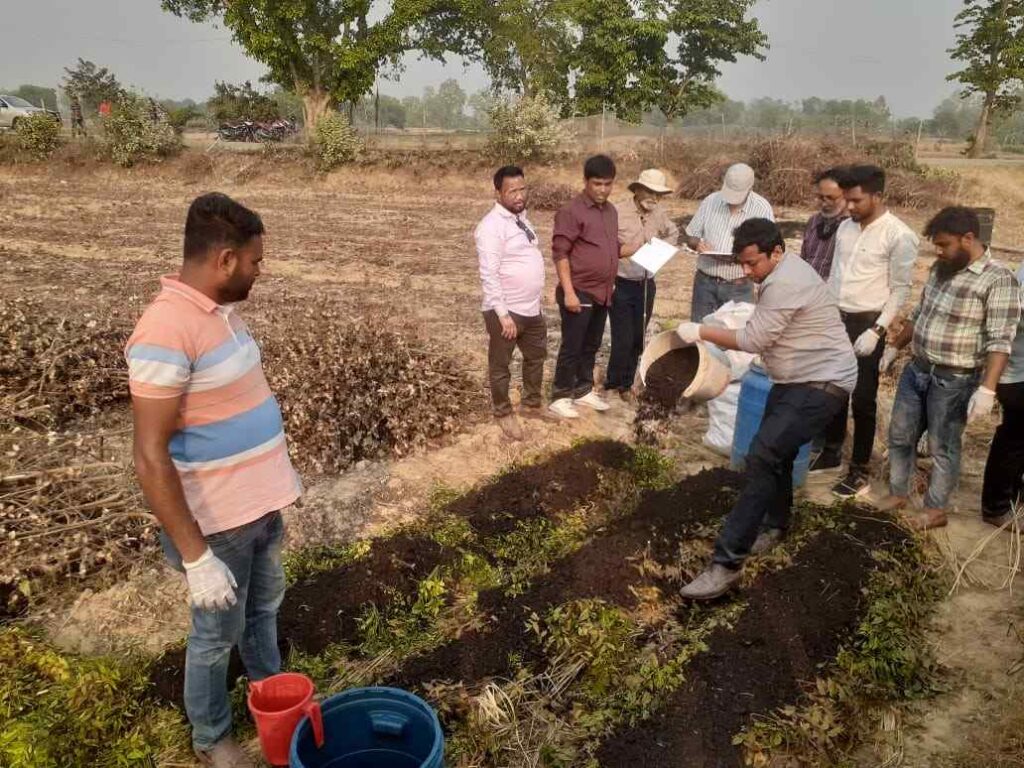






Livestock Network
Livestock Feed Store Near Me
The amount of land you have will determine that. If you have little land, chickens are probably the best choice. With enough land, you can graze cattle with minimal feeding costs. For many years, I owned a house on 30 acres of forest in the country. Each year, I take two deer, two turkeys, rabbits, and squirrels at no cost beyond the hunting license.
What Is A Way To Prevent Soil Erosion
- More trees should be planted (afforestation).
- Make a lawn and shrubs. Wind and water are the main causes of soil erosion. Roots hold the soil together, while leaves block rain and keep soil from eroding.
- Rocks or mulch can be added. This weight on the soil will protect seeds and young plants from being washed away.
- Make sure the soil is covered all year long. The ground cover protects soil from erosion. All grazing lands should have at least 30% ground cover, ideally 40%
How To Increase Acidity In Soil
Aluminum Sulphate granules, available at garden supply stores, can be used. The instructions on the package will help you know what intervals to follow each time you use them.
Livestock Vet Near Me
Depending on the clinic, I am sure. The clinic where I worked required certification for veterinary technicians. Assistants did not perform procedures such as drawing blood or cleaning teeth. Many clinics do not require vet techs to have degrees, so veterinary assistants may also perform tasks that vet techs traditionally handle. Here is a description of my experience.
Regenerative Agriculture Gallery
The Sustainable Solutions
Natural Farming
Permaculture
Organic Farming
Conservation Agriculture
Carbon Farming
Regenerative Agriculture
Biological Farming
Ecological Farming
Spiritual Farming
Biodynamic Farming
Keyline Farming
Deep-Bed Farming
Syntropic Farming
Zero-Budget Natural Farming
Sustainable Initiatives
Plant Microbiome
Extensive Farming
Sustainable farming approaches prioritize building soil carbon. Experts worldwide have proposed various methods, including natural farming, permaculture, organic farming, conservation agriculture, and regenerative agriculture. These approaches typically mimic natural ecosystems, minimize soil disturbance, and reject synthetic toxic substances. Recent sustainable initiatives strive to balance modern technologies with natural farming, aiming to rebuild ecology, rejuvenate soils, and emphasize social principles. We will explore key leaders and the philosophies behind their approaches.
Natural Farming
Natural farming conserves and strengthens natural ecology and biodiversity with minimal human intervention. It emphasizes zero-tillage, avoids chemicals, and promotes crop diversity to naturally control diseases and pests.
Zero Budget Natural Farming
Zero Budget Natural Farming emphasizes four main principles: treating seeds with beejamrut, using jeevamrut as a soil inoculant, applying achadana as bio-mulch, and employing whapsa to build soil moisture. The approach includes zero-tillage, rotating cover crops, and using biopesticides like agni-astra and brahmastra, made from vegetables and natural herbs. The Government of India aggressively promotes Zero Budget Natural Farming.

Natural Farming





















